Hyperpigmentation in Dogs [Causes & Treatments]
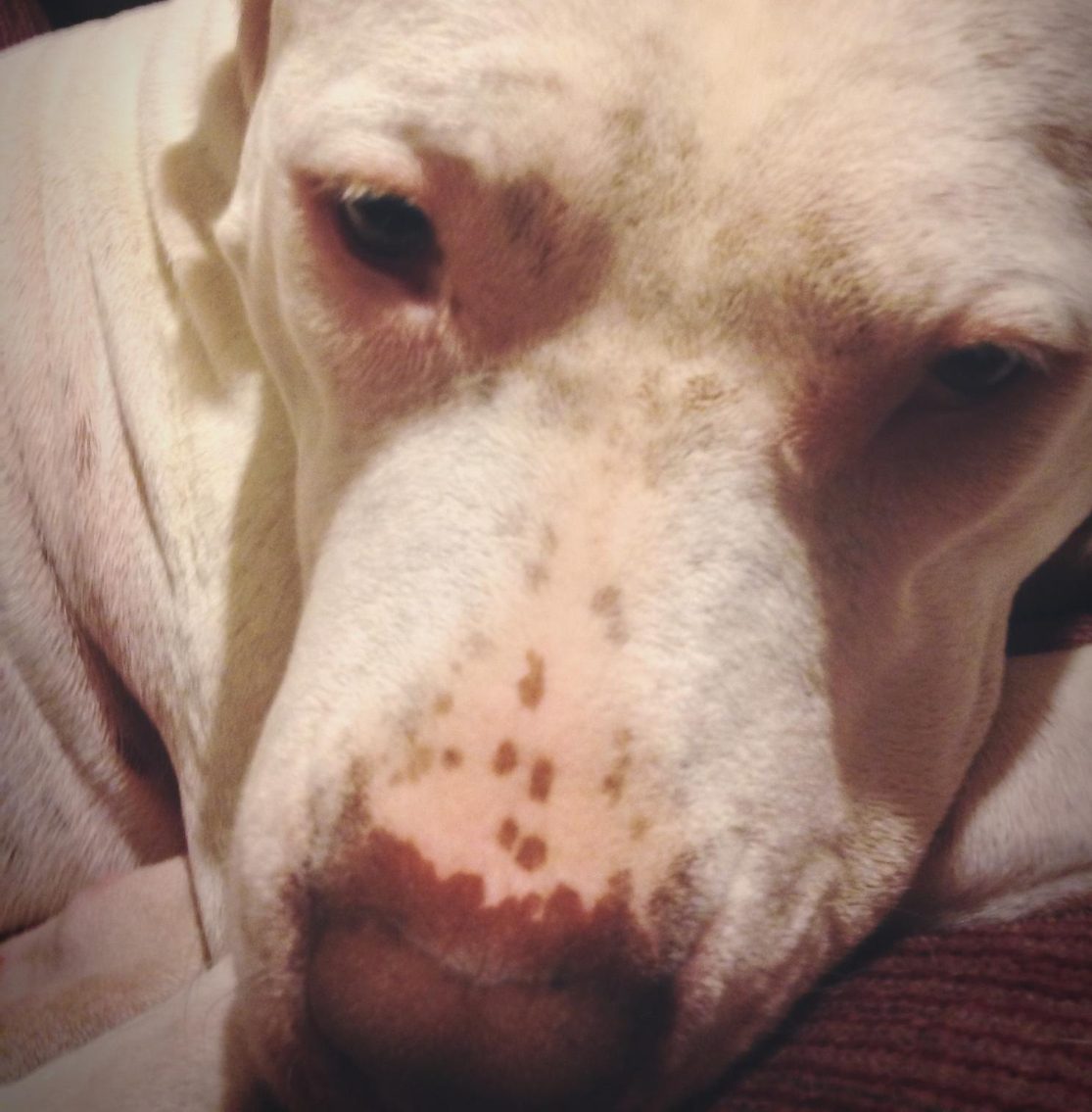

Hyperpigmentation in dogs is a condition when the skin becomes darker and often thicker than usual. This change in color and texture can affect small patches or larger areas of the dog’s body. It’s not a disease in itself but rather a symptom that can indicate an underlying issue. In this article, we’ll learn more about symptoms, causes, and treatments for hyperpigmentation in dogs.
Identifying the Signs of Hyperpigmentation in Dogs
Hyperpigmentation in dogs can appear in a number of different ways. There are various signs to look out for:
- Darkened skin patches: One of the most obvious signs of hyperpigmentation is the presence of dark, irregularly shaped patches on your dog’s skin. These patches can appear anywhere on the body, including the belly, armpits, groin area, or even the face.
- Thickened or leathery skin: In some cases, the hyperpigmented areas may feel thicker or leathery to the touch, which indicates a potential underlying skin condition.
- Hair loss or thinning: Hyperpigmentation can sometimes be accompanied by hair loss or thinning in the affected areas, which reveals the discolored skin beneath.
- Itching or irritation: Some dogs may experience itching, redness, or irritation in the hyperpigmented regions, which can lead to excessive scratching or licking.
- Gradual darkening: You may notice a gradual darkening of your dog’s skin over time rather than distinct patches.
Is Hyperpigmentation in Dogs Dangerous?
In most cases, hyperpigmentation in dogs is not inherently dangerous or life-threatening. However, it can be a symptom of an underlying health condition or a side effect of certain medications or treatments. Some potential risks associated with hyperpigmentation may include:
- Skin infections: Hyperpigmented areas can be more susceptible to bacterial or fungal infections, especially if the skin is irritated or broken due to excessive scratching or licking.
- Hormonal imbalances: Certain hormonal disorders, such as Cushing’s disease or hypothyroidism, can cause hyperpigmentation as a secondary symptom.
- Allergies or skin conditions: Hyperpigmentation can manifest as allergies, dermatitis, or other skin conditions requiring proper treatment.
- Cancerous growths: In rare cases, hyperpigmented spots may indicate cancerous growths or tumors, which require prompt medical attention.
Common Causes of Hyperpigmentation in Dogs
Hyperpigmentation can be caused by several underlying issues, from hormonal imbalances to environmental factors. Common causes may include:
- Hormonal imbalances: Conditions such as Cushing’s disease, hypothyroidism, or other endocrine disorders can lead to excessive melanin production and hyperpigmentation.
- Allergies: Food, environmental, or flea allergies can trigger skin irritation and subsequent hyperpigmentation.
- Friction or trauma: Constant friction or trauma to certain areas of the skin, such as from collar rubbing or excessive licking, can cause hyperpigmentation.
- Genetics: Some breeds, such as Dachshunds, Doberman Pinschers, and Rottweilers, may be genetically predisposed to hyperpigmentation.
- Medications: Certain medications, including some antibiotics, anti-seizure drugs, and chemotherapy drugs, can cause hyperpigmentation as a side effect.
- Aging: As dogs age, their skin may naturally produce more melanin, leading to a gradual darkening or the appearance of age spots.
- Exposure to sunlight: In areas with thin or no hair, prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation can trigger melanin production and hyperpigmentation.
- Underlying skin conditions: Conditions like dermatitis, bacterial or fungal infections, or autoimmune disorders can sometimes lead to hyperpigmentation.
Treating Hyperpigmentation in Dogs: Medications and Topical Treatments
Should you notice that your dog may have hyperpigmentation, it is recommended that you consult with your veterinarian. Your vet may recommend various medications or other treatment options, such as:
- Topical creams and ointments: Prescription-strength hydrocortisone creams or ointments containing ingredients like tretinoin or hydroquinone can help lighten hyperpigmented areas when applied topically.
- Oral medications: Depending on the underlying cause, your veterinarian may prescribe antibiotics for bacterial infections, antifungal drugs for fungal infections, or corticosteroids for inflammatory conditions.
- Hormone therapy: If a hormonal imbalance causes hyperpigmentation, your veterinarian may recommend hormone replacement therapy or other medications to regulate hormone levels.
- Cryotherapy: In some cases, cryotherapy (freezing) may be used to remove small, localized areas of hyperpigmentation.
- Laser therapy: Laser treatments can effectively reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation by targeting and breaking down excess melanin in the skin.
Preventing Hyperpigmentation in Dogs
Here are some steps you can take to reduce the risk or prevent further discoloration:
- Protect from sun exposure: Limit your dog’s exposure to direct sunlight, especially during peak hours, and consider using pet-safe sunscreen on areas with thin or no hair.
- Manage underlying conditions: If hyperpigmentation is caused by an underlying health condition, such as allergies or hormonal imbalances, work with your veterinarian to address the root cause.
- Provide a balanced diet: A nutritious, well-balanced diet can support overall skin health and potentially reduce the risk of hyperpigmentation.
- Minimize friction and trauma: Use properly fitted collars and harnesses to prevent rubbing or chafing and address any excessive licking or scratching behavior.
- Regular grooming and skin care: Regular grooming and gentle skin care can help identify and address potential issues early, preventing further discoloration.
- Avoid harsh chemicals or irritants: Steer clear of harsh chemicals, soaps, or irritants that could potentially damage or irritate your dog’s skin, leading to hyperpigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation in dogs can indicate various underlying health issues, and addressing it promptly is crucial for your pet’s well-being. Understanding the causes and treatments of hyperpigmentation helps ensure your dog receives the appropriate care.
However, managing your pet’s health often involves unexpected costs, whether for specialized treatments or ongoing care. That’s why having Pet insurance can alleviate the financial burden of veterinary care, so you can ensure you provide the best treatment for conditions like hyperpigmentation without worrying about the costs.